Fast method for measuring the Sr-90 activity with Cherenkov radiation in
silica aerogel
Povzetek
Cerenkovo sevanje, ki ga v prozorni snovi povzrocijo hitri nabiti delci, je temelj razlicnih
metod za detekcijo in identifikacijo delcev. Kot izvore Cerenkovega sevanja so do sedaj
uporabljali plinske in trdne (oziroma tekoce) sevalce. Prag za sevanje fotonov je za pione
v plinskih sevalcih nad 2,5 GeV/c, v trdnih (teko?ih) pa pod 0,2 GeV/c, medtem ko vmesno
podrocje ostane nepokrito. Gre za kinematicno obmo?je, ki je bistveno pri proucevanju
redkih razpadov mezonov B. Ti procesi so predmet raziskav vecih eksperimentov, od teh
nekateri ze potekajo, drugi pa so v pripravi. Resitev prinasa silicijev aerogel, porozna snov
z lomnim kolicnikom med 1,005 in 1,06. Rezultati, dobljeni pri eksperimentih HERMES in
BELLE kazejo, da bi bilo smiselno tak sevalec uporabiti tudi v detektorju Cerenkovih
obrocev s tankim sevalcem brez fokusiranja s sistemom zrcal (t.i. proximity focusing
RICH). Prednost takega tipa detektorjev je v kompaktnosti, ki je posebej pomembna pri
spektrometrih ob visokoenergijskih trkalnikih. Z uporabo boljsih aerogelov ter v zadnjem
casu razvitih vecanodnih fotopomno?evalk nameravamo razviti uporabno metodo za
detekcijo Cerenkovih fotonov. Pri tem bomo za odpravo ucinka neaktivne povrsine
fotopomnozevalk uporabili sistem zbiralnih lec.
Razvoj stevca Cerenkovih fotonov ponuja potencialno uporabo pri detekciji izvorov beta.
Posebej zanimiva je detekcija visoko radiotoksicnega izotopa Sr-90 v okolju. Z izbiro
aerogela s primernim lomnim kolicnikom lahko dosezemo, da le beta elektroni z dovolj
visoko energijo sevajo cerenkove fotone, tako je na primer prag v aerogelu z lomnim
kolicnikom n=1,06 pri 1 MeV. Na ta nacin lahko locimo prispevke razlicnih radioaktivnih
izotopov. V okviru predlaganega projekta bomo z modeliranjem fizikalnih procesov, ki jih
povzrocijo beta elektroni, ter ozadja zarkov gama in kozmicnih delcev, optimizirali
parametre detektorja.
Summary
Cherenkov radiation caused by fast charged particles in a transparent medium is the basis
for different methods of particle identifiaction. Up to the present, gaseous and solid (or
liquid) radiators have been used as sources of Cherenkov radiation. The threshold for
photon emission of pions is above 2.5 GeV/c in gases and below 0.2 GeV/c in solids (or
liquids). The intermediate uncovered gap is essential for the investigation of rare B meson
decays, which are the research subject of many experiments, some in progress, others in
preparation. A solution to the problem is offered by silica aerogels, a porous material with
refractive index between 1.005 and 1.06. The results obtained in two particle physics
experiments, HERMES and BELLE indicate that it would be meaningful to use such a
radiator also in Cherenkov detectors with thin radiators without focusing systems of
mirrors (so called proximity focusing RICH).The advantage of such detectors is their
compactness, which is especially important for experiments at the high energy colliders.
By making use of improved aerogels, recently developed multianode photomultiplier tubes
and additional lens systems for elimination of the inefficiency due to the PMT inactive
surface, we propose to develop a method for detection of Cherenkov photons.
A possible application of the Cherenkov photon detector could be for detection of beta
particles. Of special interest is the detection of the highly radiotoxic isotope Sr-90 in the
environment. A choice of aerogel with suitable refractive index allows one to select the
threshold energy of beta electrons, which would radiate Cherenkov photons. Thus one may
separate the contributions of different radioactive isotopes, in particular the rather
energetic ones from Sr-90 daughter isotope Y-90. By modeling the physical processes
produced by beta electrons and the gamma and cosmic ray backgrounds, we intend to
optimize the detector parameters to allow for quick measurements of low activities of the
isotope Sr-90 in environmental samples.
Less is
more with aerogels
Description of the technique - poster
Application for the project at MSZS , II , I
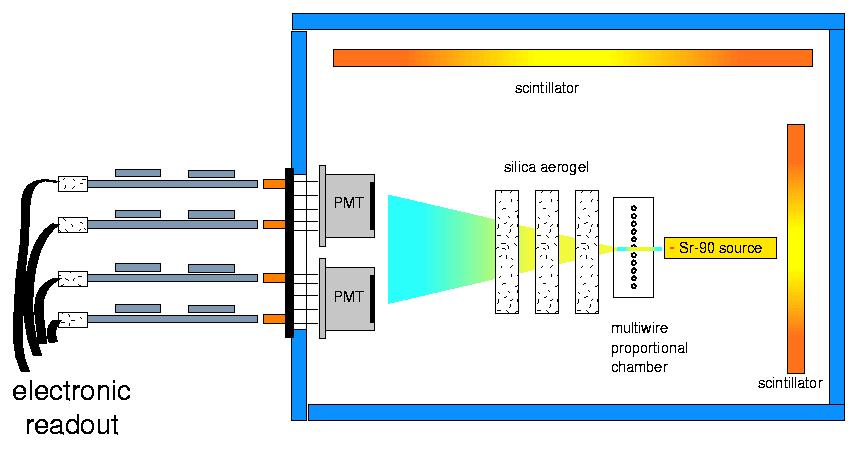
Current setup:
Strontium 90
 Toxicity Summary for STRONTIUM-90
Toxicity Summary for STRONTIUM-90
Silica aerogels references
 Recent results on aerogel development for use in Cherenkov counters , NIM A494 p.491
Recent results on aerogel development for use in Cherenkov counters , NIM A494 p.491
 Measurement of the dispersion law for hydrophobic silica aerogel SP-25 , NIM A480 (2002) p.456
Measurement of the dispersion law for hydrophobic silica aerogel SP-25 , NIM A480 (2002) p.456
 Silica Aerogel
Silica Aerogel
 Silica Aerogel
Silica Aerogel
 Properties of silica aerogels
Properties of silica aerogels 
 E. Aschenauer eta al., Optical characterisation of n=1.03 silica aerogel used as a radiator in the RICH of HERMES, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A440 (2000) p.338
E. Aschenauer eta al., Optical characterisation of n=1.03 silica aerogel used as a radiator in the RICH of HERMES, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A440 (2000) p.338
 R. De Leo et al., Chromatic aberration and forward scattering of light in silica aerogel, NIM A457 (2001) p.52
R. De Leo et al., Chromatic aberration and forward scattering of light in silica aerogel, NIM A457 (2001) p.52
 A.R.Buzykaev et al., Measurements of optical parameters of aerogel, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A433 p.396-400
A.R.Buzykaev et al., Measurements of optical parameters of aerogel, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A433 p.396-400
 T. Sumiyoshi et al., Silica aerogel Cherenkov counter for the KEK B-factory experiment, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A433 (1999) 385-391
T. Sumiyoshi et al., Silica aerogel Cherenkov counter for the KEK B-factory experiment, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A433 (1999) 385-391
Reconstruction
 J.Pinto.Cunha et al., On the reconstruction of Cherenkov rings from aerogel radiators NIM A452 (2000) p.401-421
J.Pinto.Cunha et al., On the reconstruction of Cherenkov rings from aerogel radiators NIM A452 (2000) p.401-421
Sr references
 K.Walter et al.,Simultaneous Determination of Strontium-90 and Strontium-89 by Cerenkov-Radiation and Liquid-Scintillation Counting: a Re-Evaluation for Low-Level Counting Radiochimica Acta 62 (1993) p.207-212
K.Walter et al.,Simultaneous Determination of Strontium-90 and Strontium-89 by Cerenkov-Radiation and Liquid-Scintillation Counting: a Re-Evaluation for Low-Level Counting Radiochimica Acta 62 (1993) p.207-212


Photon detector references
 P. Krizan, Tests of a multianode
PMT for the HERA-B RICH, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A394 (1997) 27-34
P. Krizan, Tests of a multianode
PMT for the HERA-B RICH, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A394 (1997) 27-34
 I.Arinyo et al.: The HERA-B RICH, October 2000, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. in Phys. Res. A453 (2000) 289-295
I.Arinyo et al.: The HERA-B RICH, October 2000, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. in Phys. Res. A453 (2000) 289-295
 S. Korpar, Multianode Photomultipliers
as Position Sensitive Detectors of Single Photons, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A442 (2000) 316-321
S. Korpar, Multianode Photomultipliers
as Position Sensitive Detectors of Single Photons, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A442 (2000) 316-321
 S. Korpar et al., The HERA-B RICH , Nucl. Instr. and Meth. in Phys. Res. A433 (1999) 128-135
S. Korpar et al., The HERA-B RICH , Nucl. Instr. and Meth. in Phys. Res. A433 (1999) 128-135
Related:
 Toru Iijima, Aerogel Cherenkov Counter in Imaging Mode JPS meeting, September 23, 1997, Tokyo Metropolitan Univ.
Toru Iijima, Aerogel Cherenkov Counter in Imaging Mode JPS meeting, September 23, 1997, Tokyo Metropolitan Univ.


 Toxicity Summary for STRONTIUM-90
Toxicity Summary for STRONTIUM-90
 Recent results on aerogel development for use in Cherenkov counters , NIM A494 p.491
Recent results on aerogel development for use in Cherenkov counters , NIM A494 p.491
 Measurement of the dispersion law for hydrophobic silica aerogel SP-25 , NIM A480 (2002) p.456
Measurement of the dispersion law for hydrophobic silica aerogel SP-25 , NIM A480 (2002) p.456
 Silica Aerogel
Silica Aerogel
 Silica Aerogel
Silica Aerogel
 Properties of silica aerogels
Properties of silica aerogels 
 E. Aschenauer eta al., Optical characterisation of n=1.03 silica aerogel used as a radiator in the RICH of HERMES, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A440 (2000) p.338
E. Aschenauer eta al., Optical characterisation of n=1.03 silica aerogel used as a radiator in the RICH of HERMES, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A440 (2000) p.338
 R. De Leo et al., Chromatic aberration and forward scattering of light in silica aerogel, NIM A457 (2001) p.52
R. De Leo et al., Chromatic aberration and forward scattering of light in silica aerogel, NIM A457 (2001) p.52
 A.R.Buzykaev et al., Measurements of optical parameters of aerogel, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A433 p.396-400
A.R.Buzykaev et al., Measurements of optical parameters of aerogel, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A433 p.396-400
 T. Sumiyoshi et al., Silica aerogel Cherenkov counter for the KEK B-factory experiment, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A433 (1999) 385-391
T. Sumiyoshi et al., Silica aerogel Cherenkov counter for the KEK B-factory experiment, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A433 (1999) 385-391
 J.Pinto.Cunha et al., On the reconstruction of Cherenkov rings from aerogel radiators NIM A452 (2000) p.401-421
J.Pinto.Cunha et al., On the reconstruction of Cherenkov rings from aerogel radiators NIM A452 (2000) p.401-421
 K.Walter et al.,Simultaneous Determination of Strontium-90 and Strontium-89 by Cerenkov-Radiation and Liquid-Scintillation Counting: a Re-Evaluation for Low-Level Counting Radiochimica Acta 62 (1993) p.207-212
K.Walter et al.,Simultaneous Determination of Strontium-90 and Strontium-89 by Cerenkov-Radiation and Liquid-Scintillation Counting: a Re-Evaluation for Low-Level Counting Radiochimica Acta 62 (1993) p.207-212


 P. Krizan, Tests of a multianode
PMT for the HERA-B RICH, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A394 (1997) 27-34
P. Krizan, Tests of a multianode
PMT for the HERA-B RICH, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A394 (1997) 27-34
 I.Arinyo et al.: The HERA-B RICH, October 2000, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. in Phys. Res. A453 (2000) 289-295
I.Arinyo et al.: The HERA-B RICH, October 2000, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. in Phys. Res. A453 (2000) 289-295
 S. Korpar, Multianode Photomultipliers
as Position Sensitive Detectors of Single Photons, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A442 (2000) 316-321
S. Korpar, Multianode Photomultipliers
as Position Sensitive Detectors of Single Photons, Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A442 (2000) 316-321
 S. Korpar et al., The HERA-B RICH , Nucl. Instr. and Meth. in Phys. Res. A433 (1999) 128-135
S. Korpar et al., The HERA-B RICH , Nucl. Instr. and Meth. in Phys. Res. A433 (1999) 128-135
 Toru Iijima, Aerogel Cherenkov Counter in Imaging Mode JPS meeting, September 23, 1997, Tokyo Metropolitan Univ.
Toru Iijima, Aerogel Cherenkov Counter in Imaging Mode JPS meeting, September 23, 1997, Tokyo Metropolitan Univ.