#ifndef __CINT__
#include "RooGlobalFunc.h"
#endif
#include "RooDataSet.h"
#include "RooRealVar.h"
#include "RooGaussian.h"
#include "RooAddPdf.h"
#include "RooProdPdf.h"
#include "RooAddition.h"
#include "RooProduct.h"
#include "TCanvas.h"
#include "RooChebychev.h"
#include "RooAbsPdf.h"
#include "RooFit.h"
#include "RooFitResult.h"
#include "RooPlot.h"
#include "RooAbsArg.h"
#include "RooWorkspace.h"
#include "RooStats/ProfileLikelihoodCalculator.h"
#include "RooStats/HypoTestResult.h"
#include <string>
using namespace RooFit;
using namespace RooStats;
void AddModel(RooWorkspace*);
void AddData(RooWorkspace*);
void DoHypothesisTest(RooWorkspace*);
void MakePlots(RooWorkspace*);
void rs102_hypotestwithshapes() {
RooWorkspace* wspace = new RooWorkspace("myWS");
AddModel(wspace);
AddData(wspace);
DoHypothesisTest(wspace);
MakePlots(wspace);
delete wspace;
}
void AddModel(RooWorkspace* wks){
Double_t lowRange = 60, highRange = 200;
RooRealVar invMass("invMass", "M_{inv}", lowRange, highRange,"GeV");
RooRealVar mH("mH","Higgs Mass",130,90,160) ;
RooRealVar sigma1("sigma1","Width of Gaussian",12.,2,100) ;
RooGaussian sigModel("sigModel", "Signal Model", invMass, mH, sigma1);
mH.setConstant();
sigma1.setConstant();
RooRealVar mZ("mZ", "Z Mass", 91.2, 0, 100);
RooRealVar sigma1_z("sigma1_z","Width of Gaussian",10.,6,100) ;
RooGaussian zjjModel("zjjModel", "Z+jets Model", invMass, mZ, sigma1_z);
mZ.setConstant();
sigma1_z.setConstant();
RooRealVar a0("a0","a0",0.26,-1,1) ;
RooRealVar a1("a1","a1",-0.17596,-1,1) ;
RooRealVar a2("a2","a2",0.018437,-1,1) ;
RooRealVar a3("a3","a3",0.02,-1,1) ;
RooChebychev qcdModel("qcdModel","A Polynomail for QCD",invMass,RooArgList(a0,a1,a2)) ;
a0.setConstant();
a1.setConstant();
a2.setConstant();
RooRealVar fzjj("fzjj","fraction of zjj background events",.4,0.,1) ;
RooRealVar fsigExpected("fsigExpected","expected fraction of signal events",.2,0.,1) ;
fsigExpected.setConstant();
RooRealVar mu("mu","signal strength in units of SM expectation",1,0.,2) ;
RooRealVar ratioSigEff("ratioSigEff","ratio of signal efficiency to nominal signal efficiency",1. ,0.,2) ;
ratioSigEff.setConstant(kTRUE);
RooProduct fsig("fsig","fraction of signal events",RooArgSet(mu,ratioSigEff,fsigExpected)) ;
RooAddPdf model("model","sig+zjj+qcd background shapes",RooArgList(sigModel,zjjModel, qcdModel),RooArgList(fsig,fzjj)) ;
wks->import(model);
}
void AddData(RooWorkspace* wks){
Int_t nEvents = 150;
RooAbsPdf* model = wks->pdf("model");
RooRealVar* invMass = wks->var("invMass");
RooDataSet* data = model->generate(*invMass,nEvents);
wks->import(*data, RenameDataset("data"));
}
void DoHypothesisTest(RooWorkspace* wks){
ProfileLikelihoodCalculator plc;
plc.SetWorkspace(*wks);
plc.SetCommonPdf("model");
plc.SetData("data");
RooRealVar* mu = wks->var("mu");
RooArgSet* nullParams = new RooArgSet("nullParams");
nullParams->addClone(*mu);
nullParams->setRealValue("mu",0);
plc.SetNullParameters(*nullParams);
HypoTestResult* htr = plc.GetHypoTest();
cout << "-------------------------------------------------" << endl;
cout << "The p-value for the null is " << htr->NullPValue() << endl;
cout << "Corresponding to a signifcance of " << htr->Significance() << endl;
cout << "-------------------------------------------------\n\n" << endl;
}
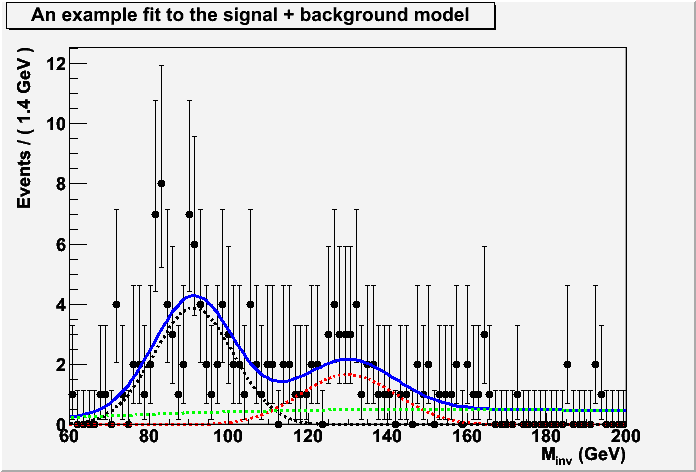
void MakePlots(RooWorkspace* wks) {
RooAbsPdf* model = wks->pdf("model");
RooAbsPdf* sigModel = wks->pdf("sigModel");
RooAbsPdf* zjjModel = wks->pdf("zjjModel");
RooAbsPdf* qcdModel = wks->pdf("qcdModel");
RooRealVar* mu = wks->var("mu");
RooRealVar* invMass = wks->var("invMass");
RooAbsData* data = wks->data("data");
mu->setConstant(kFALSE);
RooFitResult* fitResult = model->fitTo(*data,Save(kTRUE),Minos(kFALSE), Hesse(kFALSE),PrintLevel(-1));
TCanvas* cdata = new TCanvas();
RooPlot* frame = invMass->frame() ;
data->plotOn(frame ) ;
model->plotOn(frame) ;
model->plotOn(frame,Components(*sigModel),LineStyle(kDashed), LineColor(kRed)) ;
model->plotOn(frame,Components(*zjjModel),LineStyle(kDashed),LineColor(kBlack)) ;
model->plotOn(frame,Components(*qcdModel),LineStyle(kDashed),LineColor(kGreen)) ;
frame->SetTitle("An example fit to the signal + background model");
frame->Draw() ;
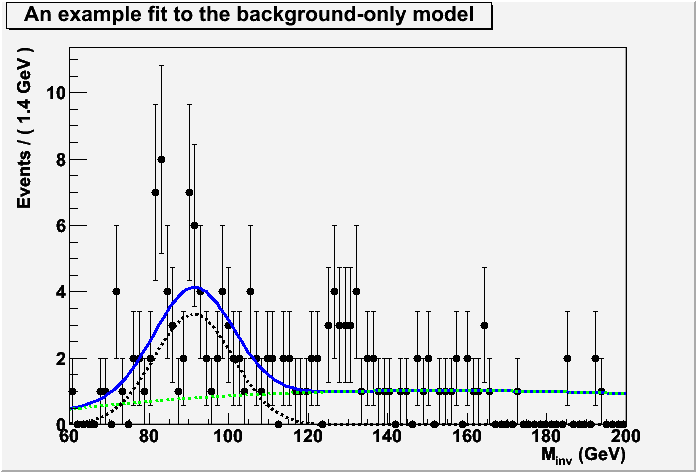
mu->setVal(0);
mu->setConstant(kTRUE);
RooFitResult* fitResult2 = model->fitTo(*data, Save(kTRUE), Minos(kFALSE), Hesse(kFALSE),PrintLevel(-1));
TCanvas* cbkgonly = new TCanvas();
RooPlot* xframe2 = invMass->frame() ;
data->plotOn(xframe2, DataError(RooAbsData::SumW2)) ;
model->plotOn(xframe2) ;
model->plotOn(xframe2, Components(*zjjModel),LineStyle(kDashed),LineColor(kBlack)) ;
model->plotOn(xframe2, Components(*qcdModel),LineStyle(kDashed),LineColor(kGreen)) ;
xframe2->SetTitle("An example fit to the background-only model");
xframe2->Draw() ;
}
|
|